Have a Question?
Understanding Dehydration in Older Adults
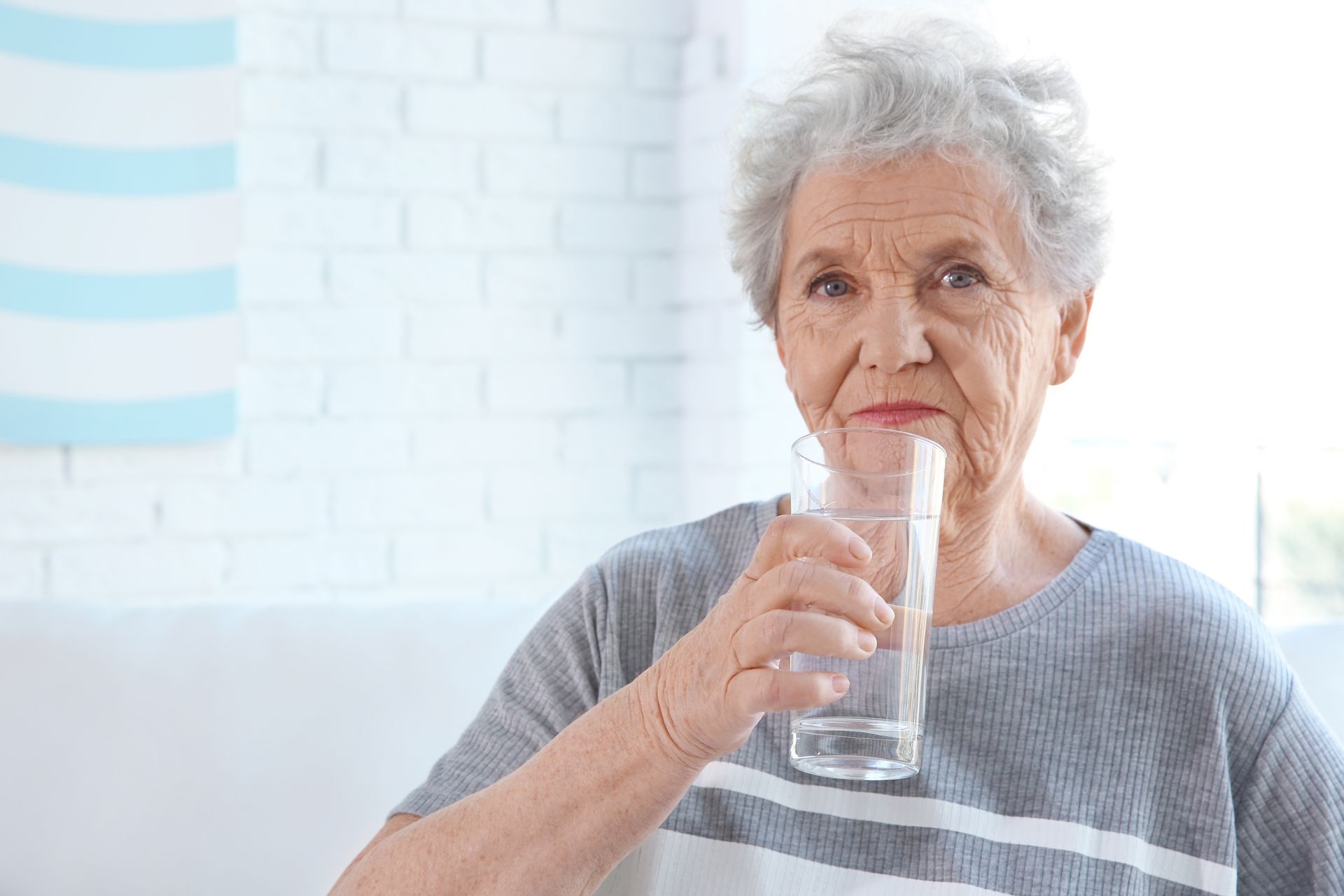

Water is essential for sustaining every cell, tissue, and organ in our bodies. While hydration is crucial for everyone, older adults are particularly vulnerable to dehydration due to age-related bodily changes. Many people aged 65 and older don’t drink enough water, with up to 40% of community-dwelling elderly potentially being chronically under hydrated. This can lead to severe dehydration, infections, and other health problems. Understanding and meeting specific water needs is vital for ensuring optimal health and well-being in older adults.
The Role of Water in the Body
Water is fundamental for maintaining the health and functionality of every cell, tissue, and organ. It regulates body temperature, aids digestion, transports nutrients and oxygen, flushes out toxins, lubricates joints, and supports skin health.
Why Dehydration is a Concern for Older Adults
Older adults are particularly vulnerable to dehydration due to several factors:
Reduced Thirst Sensation
As people age, the sensation of thirst diminishes, leading to lower water intake.
Body Composition Changes
Aging results in a lower water content in the body.
Medication
Many seniors take medications that increase the risk of dehydration.
Temperature Regulation
Older adult’s bodies don't regulate temperature as efficiently, increasing the risk during physical activities.
Cognitive Performance
Dehydration negatively affects cognitive function, increasing the risk of metabolic and renal diseases.
Symptoms of Dehydration
Recognising the early signs of dehydration is crucial.
Dark urine and infrequent urination
Fatigue and weakness
Irritability
Dizziness and headaches
Muscle cramps
Dry mouth
Confusion and decreased cognitive function
Older Adults and Hydration
Older adults are at higher risk of dehydration due to health conditions, medications, loss of muscle mass, and reduced kidney function. Staying well-hydrated can lead to fewer falls, less constipation, and a lower risk of bladder cancer in men. Dehydration in older adults is linked to increased urinary tract infections, confusion, kidney failure, and slower wound healing. Ensuring proper hydration can significantly improve health outcomes and quality of life for older adults.
How Much Water Do You Need?
The amount of water each person needs varies based on age, weight, climate, and activity level. Generally, aiming for at least 8 glasses of water per day is recommended, but individual needs can differ. For adults over 65, the recommended intake is about 2.7 liters (11.5 cups) per day for women and 3.7 liters (15.5 cups) per day for men, including water from all beverages and foods.
Factors Affecting Water Needs
Individual water needs can vary based on several factors:
Climate
Hot or humid weather can increase the need for water intake.
Physical Activity
More active individuals may require additional water to compensate for fluid loss through sweat.
Health Conditions
Certain conditions, such as fever, diarrhoea, and urinary tract infections, can increase water needs.
Diet
High-protein, high-fibre, or salty foods can increase the need for water.
Tips for Preventing Dehydration
The best way to prevent dehydration is to drink water regularly throughout the day. Here are some tips.
Drink Regularly
Don't wait until you're thirsty. Make it a habit to drink water regularly throughout the day.
Use a Water Bottle
Carrying a reusable water bottle helps you drink more consistently.
Set Reminders
Use phone apps or alarms to remind you to drink water.
Eat Hydrating Foods
Incorporate water-rich fruits and vegetables like cucumbers, oranges, and watermelon into your diet.
Flavour Your Water
Adding natural flavours like lemon, lime, or cucumber can make drinking water more enjoyable.
Monitor Your Urine
Light-coloured urine typically indicates adequate hydration, while dark urine can be a sign that you need to drink more water.
Conclusion
Water is essential for overall health and well-being. Understanding its crucial role and making a conscious effort to stay hydrated can lead to significant health benefits, particularly for older adults. Prioritising hydration helps in maintaining better physical and mental health.

About
INS LifeGuard is the only 24/7 nurse on-call personal and medical monitoring in Australia. We provide monitoring technology for both in the home and on the go and can also monitor other provider's equipment. Our services are suitable for anyone wanting support to stay independent such as the elderly, those with medical conditions and disabilities plus enhancing safety and security for lone workers.